'Worrisome' deadly fungus spreading through US at alarming rate
The fungus, Candida auris, was identified in Asia in 2009 but was first reported in the US in 2016. The number of infections in the country has risen by 95% between 2020 and 2021.
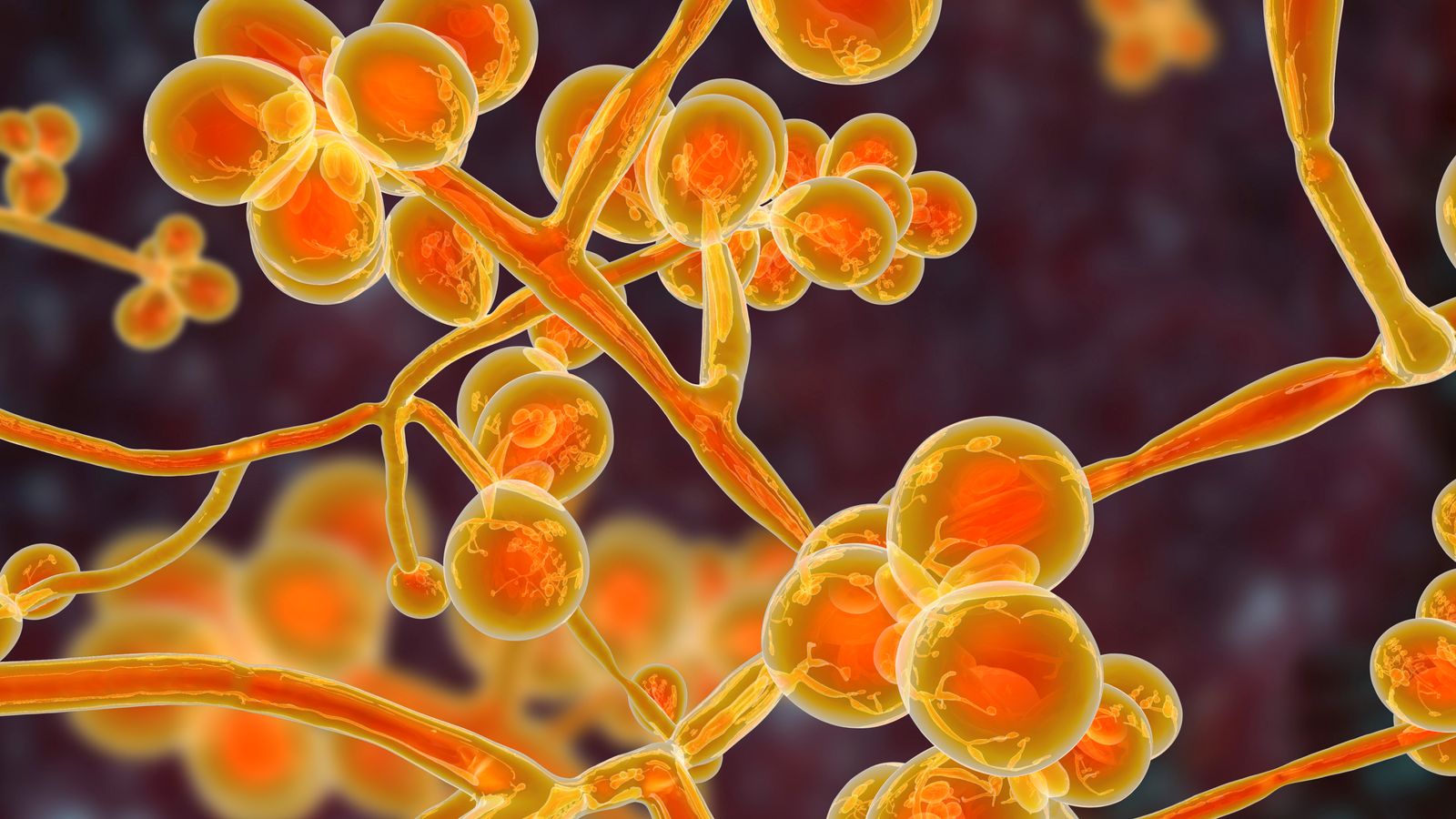
A drug-resistant and potentially deadly fungus is spreading rapidly through US health facilities, according to a government study.
Researchers from the Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reported the fungus, a type of yeast called Candida auris or C. auris, can cause severe illness in people with weakened immune systems.
The number of people diagnosed, as well as the number who were found through screening to be carrying C. auris, has been rising at an alarming rate since the fungus was first reported in the US in 2016.
The fungus was identified in 2009 in Asia, but scientists have said C. auris first appeared around the world about a decade earlier.
Dr Meghan Lyman, chief medical officer of the CDC's mycotic diseases branch, said the increases, "especially in the most recent years, are really concerning to us".
"We've seen increases not just in areas of ongoing transmission, but also in new areas," she said.
Dr Lyman also said she was concerned about the increasing number of fungus samples resistant to the common treatments for it.
Dr Waleed Javaid, an epidemiologist and director of infection prevention and control at Mount Sinai Downtown in New York, said the fungus was "worrisome".
"But we don't want people who watched 'The Last Of Us' to think we're all going to die," Dr Javaid said.
"This is an infection that occurs in extremely ill individuals who are usually sick with a lot of other issues."
The fungus, which can be found on the skin and throughout the body, is not a threat to healthy people.
But about one-third of people who become sick with C. auris die.
The fungus has been detected in more than half of all US states. The number of infections in the US increased by 95% between 2020 and 2021.
The new research comes as Mississippi is facing a growing outbreak of the fungus.
Since November, 12 people in the state have been infected with four "potentially associated deaths", according to the state's health department.
-sky news






