'I saw them as monsters and man-eaters': Saving the world's rarest crocodile from its bad reputation
It's known for its deadly bite, but the Philippine crocodile – thought to be the rarest in the world – has a lot more to give than it gets credit for. An effort blending science and indigenous knowledge to protect the species is helping replenish ecosystems and livelihoods.
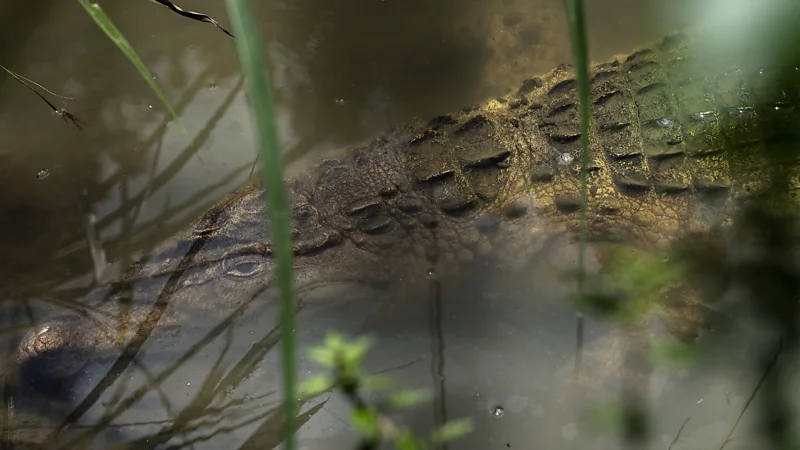

In the lush, humid forest of the Philippines' Northern Sierra Madre Natural Park, three men in shorts, T-shirts and headlamps shape themselves a path through the night's thick vegetation with long sticks. They're treading quietly, calf-deep into turbid waters, and shining their torches against the darkness whirlpooling around their feet. Then, they see it. Quickly, they snatch the slender baby crocodile straight out of the safety of its muddy pond. What they are doing is not hunting or harming the infant yet stoic creature – one of the rarest crocodile species on the planet – but rather saving it from the brink of extinction.
Throughout history, the Philippine crocodile – known to science as Crocodylus mindorensis – could be found all over the Filipino archipelago, crawling around marshes, splashing in ponds and creeks, and trailing across fast-paced rivers nestled in limestone formations across the dense forests.
Historical records show that the indigenous people of the Philippines likely feared the small reptilian predator – which they called buwaya (crocodile) and bukarot (Philippine crocodile) – yet revered, venerated and respected it, living in harmony with it. Crocodiles were a symbol of strength and power, and villagers, especially tribe chiefs and the reptiles were thought to share intimate spiritual bonds. Some ethnicities believed that their ancestors would reincarnate as crocodiles, guarding over them in the years to come. If they spotted one among the turbid waters, they'd call out to them "Nono", or grandfather.
Spear fisherfolk were known to ask the crocodiles for permission to pass through their stretches of water and share nature's bounty, according to Nestor Aliejo, a leader of the indigenous Agta community in Dunoy and Villa Miranda, in the northern Philippines. "The crocodile is not really that harmful, as long as you don't hurt them," says Aliejo.
It was likely when the Spanish colonisers of the 1560s set foot on the islands that the perception of the reptilians started shifting. Apart from getting their taxonomy wrong and not distinguishing the Philippine crocodile from the saltwater crocodiles also found in the archipelago, records show high-ranking colonial officers wrote in their letters that crocodiles were everywhere, and they were "very bloodthirsty and cruel". One church fresco from San Mariano depicts a saint saving his people by stomping on a crocodile. Historians from the 1700s described crocodiles as "monstrous caimans" who killed people, especially children. (While indigenous credence among some ethnicities was actually that crocodiles never randomly assaulted humans, but rather they acted as divine arbiters, pruning evil in society.)
Over time, the Philippine crocodile's habitat was gnawed away at consistently through agricultural and industrial development, urbanisation, mining, slash-and-burn agriculture, and, since the late 1900s, legal and illegal logging as the Philippines became one of the world's largest exporters of tropical hardwoods. The rise of aggressive overfishing techniques like electrofishing also posed a risk to the wildlife in rivers.
The buwaya became indiscriminately persecuted: they were hunted out of fear of their attacks, for fun, as well as for the trade of their meat and precious skin. Their numbers plummeted. Estimates suggest that more than 80% of all of the archipelago's crocodiles have been killed in the past century – going from around 10,000 crocodiles (although this is hard to verify) to just 100 in the wild by the early 1990s – leaving small and rare pockets of populations in secluded inland freshwater habitats.
By the 2000s, all scientists could find was 20 crocodiles split among three interconnected river systemsin the Sierra Madre Mountains in north-eastern Luzon, a fragment of population in the small island of Dalupiri, and a likely larger population on the island of Mindanao. The latter, though, has been difficult to survey given the socio-political unrest in the area and there being armed groups in the marsh.
As a result, the Philippine crocodile was quickly listed as critically endangered by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species, and experts established the Philippine Crocodile National Recovery Team to attempt to bring the crocodile back from the brink.
Action to save the crocodile took several forms. The Filipino government, universities and organisations focused on rearing Philippine crocodiles in captivity. This was already underway from 1981, when Silliman University pioneered captive breeding and, starting with two adults, they hatched 114 baby crocodiles over 13 years, then distributed them to private institutions for safekeeping and further rearing programmes.
Starting from those first crocodiles in the 1980s, local governments, non-profits and private organisations have continued a wide range of captivity rearing programmes, with mixed results. In 2010, the first ever 50 captive-bred Philippine crocodiles we reintroduced, but they all died because they were not fit enough for wild conditions and they were killed by people. Now the six crocodile farms that make up the non-profit organisation Crocodylus Porosus Philippines. lead the way on these types of reintroduction projects to the wild or semi-captive habitats. In 2013, they successfully released some crocodiles in the Paghungawan Marsh on Siargao Island, now a popular tourist attraction, and by 2021, these released crocodiles even had young in the wild.
Zoos from all over the world – including the US, Australia, and several throughout Europe – have also pitched in, even launching their own purebred C. mindorensis breeding efforts.
"We're really just trying to ensure that there is a viable population [living outside its natural habitat] that would support the wild population if that need arises," says Chris Banks, the international conservation manager at Zoos Victoria in Australia.
The day we spoke, a female Philippine crocodile was flying on a plane over to Victoria from the Cologne Zoo in Germany. (The Cologne Zoo had already sent two male crocodiles called Hulky and Dodong back to the Philippines for reintroduction in the wild in 2020.)
On the other hand, conservationists argue that captive breeding and reintroduction programmes cannot exist in a silo – especially not without mending the relationship between wild populations of crocodiles and the people with whom they share the land.
The non-profit foundation Mabuwaya – which first surveyed the crocodiles in the Sierra Madre Mountains in the 2000s, and reintroduced those first 50 captive-bred crocodiles – aims to combine conservation efforts with local indigenous knowledge to preserve the remaining C. mindorensis. Together with the Kalingha people, the Agta people, and immigrant farmers in San Mariano, they are creating buffer zones for reforestation and the reintroduction of native plants to the crocodile's habitat, and they have founded eight crocodile sanctuaries where commercial agriculture, farming and fishing are now illegal.
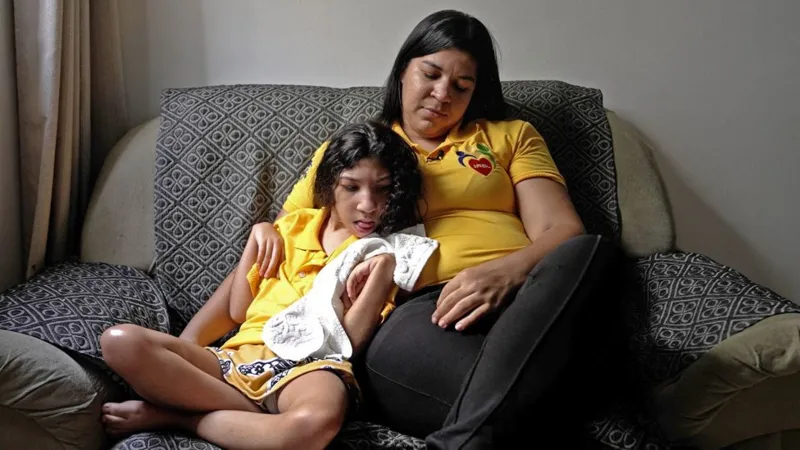
Olalia Infiel, an Agta woman from the Dunoy village, says she teaches the village youth: "Go fishing, but don't mess with the crocodiles… you should not hurt them, and they will also respect you."
Since law enforcement in these remote islands of the archipelago is scarce, these sanctuaries are run by community leaders, representatives of the local government, and 12 volunteer community leaders – some indigenous, some not – known as the Bantay Santuwaryo, or guardians of the sanctuaries. Mabuwaya trains them in population monitoring to survey the existing crocodile numbers, a task which they carry out every three months. They are also trained by lawyers on environmental law, how to collect evidence, how to confiscate incriminating materials, how to conduct a proper arrest, and how to file a case, and they are deputised by the municipal government as environmental law enforcers.
"Before there were people who were hunting crocodiles, it was normal. [Nobody said] 'that's not good', because there were no rules or laws [in] those times," says Victorino Montanes, the first local to be appointed as Bantay Santuwaryo in 2004. (It is the Wildlife Act of 2001 that made it punishable by law to kill a crocodile.)
Now, on top of their full-time jobs as fishers and farmers, Montanes and his colleagues also patrol the wetlands and rivers where the wild crocodiles reside, looking over them. Recently, the volunteers also found a deceased juvenile crocodile trapped in a fishing net next to a rice field.
Nestor Gumarang, a member of the Bantay Santuwaryo since 2016, believes authorities should "make an example of whoever kills crocodiles, they should punish or imprison them so that everybody will listen".
This type of environmental stewardship isn't just to save the crocodiles from extinction, according to Marshall Magas, an Agta man from Gab-Gab village. But rather, it is also to improve the local community's livelihood by restoring environmental equilibria and, hopefully, bringing wildlife populations back to healthier numbers.
"When I was young… I could catch a lot of fish, eels, even wild boar and other animals. But now it's very difficult," says Magas. Saving the crocodiles would potentially give life back to the local waters, also helping keep the Agta people's hunting and foraging traditions alive.
In their role as crocodile wardens, the Bantay Santuwaryo also actively help baby crocodiles make it into adulthood. Hatchlings are so small they're sometimes swept away by strong currents and killed, or easily targeted by predators like snakes, monitor lizards, birds and even huge fire ants. So the volunteers patrol the rivers at night, torches in hand, to protect the crocodile nests from destruction. They collect young hatchlings as soon as they are born, and take them to a conservation center where scientists raise them in semi-captivity until they are strong enough to be released back into the wild.
Thanks to this method, the survival rate of Philippine crocodile hatchlings in the Sierra Madre area has been 79% throughout the entirety of the headstart programme, says Merlijn Van Weerd, one of the founders of Mabuwaya Foundation. A study looking at the results of release after one year in captivity, head-started Philippine crocodile hatchling survival was 72% compared to 47% for wild hatchlings, and at least 53% of those head-started hatchling crocodiles were still alive after a year in the wild.
This population is now up to about 125 individuals, including 17 adults, 41 juveniles, and dozens of hatchlings, the Mabuwaya team says. Breeding attempts in captivity haven't been successful so far, but the conservationists are hopeful.
Still, while conservationists would love to see the crocodiles back to their original distribution – from the top of the archipelago all the way to the bottom – that'll likely not be possible, because of habitat alteration and the sheer abundance of the human population in those areas, according to Charlie Manolis, co-chair of the IUCN SSC Crocodile Specialist Group, who is not actively involved with the Mabuwaya efforts.
"The difficulty for the Philippine crocodile is that it lives in a place where there's a gazillion people," says Manolis. "Once people have gone long periods of time not having crocodilians around them, bringing them back is really, really a lot more difficult, because people don't have a living memory of living with them."
Community dedication, in fact, is key to the success of the reintroduction.
Bernard Tarun, now a biodiversity expert at the Mabuwaya Foundation, wasn't a fan of crocodiles when he started off. The first time he held a Philippine crocodile in his hands, he was bitten. But instead of shunning the creatures, he grew adamant he'd establish rapport with them, learn how to manage them, and never get bitten again. "Especially those communities living near the crocodile localities, they already changed their mind," says Tarun. "From 'Oh, you have to kill that one', now to 'Okay, don't disturb, enjoy watching the crocodile'."
Ultimately, almost all efforts of the Bantay Santuwaryo, the Mabuwaya foundation, and the Agta community go towards educational projects to change people's perception of crocodiles.
In mainstream Filipino culture, fear and negative preconceptions about the apex predators still linger: crocodiles are perceived as bloodthirsty people-eaters. In the media, corrupt politicians, self-serving government officers, or moneylenders and landlords are often referred to as buwaya in disrespect.
Instead, the indigenous Kalinga people sing about the bond between their chiefs and crocodiles, the Magindanaon people still believe they descend from crocodiles, and the Tagbanwa say their ancestors made a blood pact with the reptiles to keep them safe from their hunger.
"We have never met an Agta who hates crocodile or who would kill crocodiles," says Van Weerd. "We're trying to get that relationship back in which there is respect for the crocodiles."
So the teams have been running intensive communication, education and public-awareness campaigns, including everything from posters and calendars to radio programs, puppet shows, school visits and launching a crocodile mascot. They're also kickstarting projects on getting more women involved in biodiversity conservation – so far, the Bantay Santuwaryo only has two women on board – as well as promoting the Philippine crocodile as a tourist attraction for the area, says Marites Gatan-Balbas, one of the founders of Mabuwaya Foundation.
It was she who started the team's interest in the crocodile species when, while doing fieldwork out in Sierra Madre on March 17, 1999, a fisherman asked her to buy a C. mindorensis from him. "When they showed me the croc, I just didn't care about it, because I also saw them as monsters and man-eaters," says Gatan-Balbas. Now, though, "our slogan is 'Philippine crocodile, something to be proud of'." That fisherman used to reel in baby crocodiles as bycatch and sell them as pets. He too, now, works for the Bantay Santuaryo instead.
-BBC